Can Fish Drown In Water? The Surprising Facts
You might consider it futile to try and drown a fish in water, but there is actually a possibility of it happening. Of course, drowning for a fish does not conjure up the same fears and worries that it does for us as humans.
Don’t worry, you don’t need to go buy your fish armbands, take him to a paddling pool and teach him how to swim!
All fish are born with an innate freedom in water and an inability to survive for long periods outside of the water, but they too can suffer and even die when they are deprived of oxygen.
In this comprehensive article we will explore the science behind how a fish breathes and what it needs oxygen for, and we will answer that intriguing question, can fish drown?
What’s more, we’ll consider the precise way in which oxygen deprivation might impact them, and we’ll even have some helpful tips and tricks for you as a fish owner, to help your beloved fish avoid this fate. So dive on in!
Table of Contents
Can Fish Drown?
The sweet and simple answer to this interesting question is yes, fish can drown. However, to really understand this topic, and the related topic of oxygenation, we need to explore a bit about fish anatomy and how they differ from humans.
Firstly, there is a major difference between a fish drowning and a human drowning, although the end results might be the same.
In humans, when we take in too much water into our lungs, the water blocks the easy transfer of oxygen between the air and our body (specifically, the alveoli). This means there is no new oxygen entering the bloodstream, so our cells quickly become starved of oxygen.
This is a huge danger, because our cells need lots of oxygen to stay functioning, and without it they will simply shut down and die. If this situation is not remedied quickly by removing the water in the lungs, then death is certain.
As you might expect, the situation is somewhat different with fish. Of course, fish are suited by evolution to the water, but they still require oxygen to function. This means they have a very different system in their body for transferring oxygen to their cells.
In this case however, they extract the oxygen from the water rather than the air. However, if there is not enough oxygen present dissolved in the water, then the fish are in danger of drowning. In this case the term suffocation or asphyxiation may be more accurate, indicating a lack of oxygen intake, but people commonly use the term drowning.
As with humans, this condition can very quickly be fatal.
Why Is Oxygen So Important?
Video: “Oxygenation for beginners”
You might be surprised at the answer to the famed question, can fish drown, but the real reason is the almost universal importance of oxygen.
For aquatic creatures, all the oxygen they can access is the small portion of oxygen that is dissolved in water. This is usually called the dissolved oxygen, or DO, level. This is usually measured in ppm, meaning parts per million.
A typical level of DO is 4-8 ppm, which means there are 4 -8 molecules of oxygen present in every million molecules of water. As you can appreciate, that is not a lot!
Oxygen is very important to keep a fish’s body functioning properly. All the cells, which are the individual building blocks of living creatures, require oxygen to stay alive and healthy. They require even more oxygen when they are multiplying or growing.
Oxygen is used to help extract and store energy from food. You can consider the analogy with oil. There is lots of resident, stored energy in a container of oil, waiting to be released as heat when it is set alight. But you can’t start a fire to release that energy unless there is oxygen present.
It’s the same with cells. They require oxygen to metabolize and for all their active processes. Oxygen can also be chemically combined with other substances to help create new proteins and cell matter, and they can help to break down waste products in the body.
Overall, dissolved oxygen is of great importance to a fish, and to maintain a healthy ecosystem in your tank you need to make sure there is a sufficient level of dissolved oxygen present.
6 Easy Steps On How To Increase Oxygen in the Fish Tank
How Do Fish Harness The Oxygen?
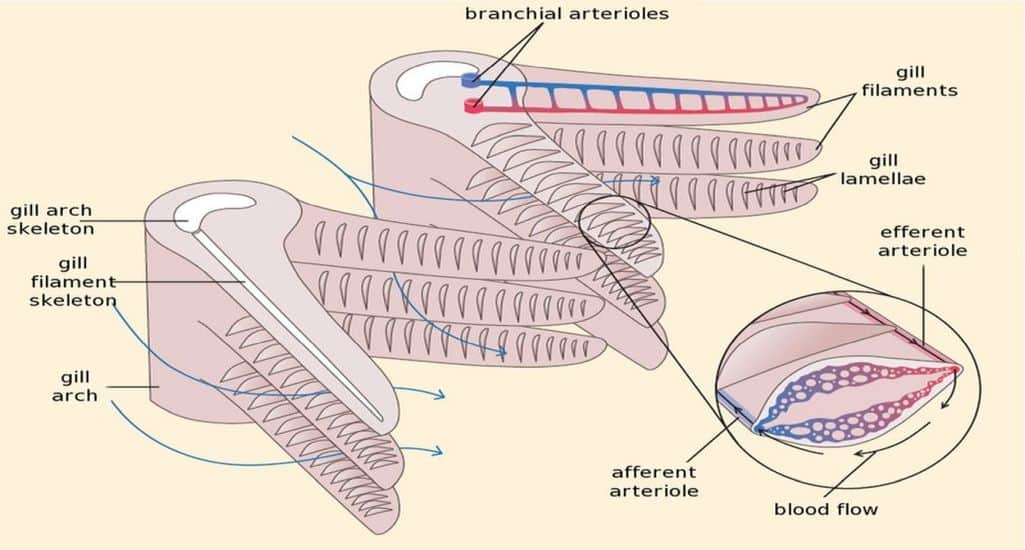
Because of the presence of water, and the relatively low concentration of oxygen, fish must gather their oxygen from the environment in a very different way than we humans do. While our lungs have evolved to be perfectly suited to the environment we live in, fish need other bodily tools.
The way most marine creatures gather oxygen for their cells is through the use of gills. Gills are very special slits on the side of a fish, and they are involved in the transport of oxygen to the inside of the body. Gills have a very special membrane in them, known as the epithelium. The epithelium is constructed to allow the oxygen molecules to pass across it, but not the water or other molecules.
The oxygen then enters into the deoxygenated blood on the other side of the gill.
From there it is carried around the body, to revive cells and keep them healthy. At the same time, one of the unwanted products of energy harvesting (also called respiration) is carbon dioxide. This carbon dioxide must be removed from the body, or else it can poison the cells. Carbon dioxide is also allowed to pass across the epithelium of the gills, to exit out into the environment.
There are a number of different ways that fish can arrange their gills, and the exact details differ from species to species. Many types of fish have 4 gills on either side of their body, and this kind of symmetry is very common. They are usually located midway up the fish, close to the fish’s mouth.
Supply Of Water
The supply of water to the gills is very important. If there is not an adequate flow of water over the gills, then they will not be able to pull enough oxygen into their body to fuel their cells. The surface area of a fish’s gill is usually quite large, especially compared to the oxygen exchange organs in a human.
There is a very good reason for this. The concentration of oxygen in air is 21 % or in other words, 210,000 ppm. Compare this to the paltry 4 – 8 ppm of DO in water and you can see that a fish needs to process a lot more water to harness the same quantity of oxygen.
Fish may use a number of different techniques to try and increase the flow of water over their gills.
For example, many fish will puff out their appendages to try and redirect greater flow to the gills. A lot of species do this by opening and closing the muscles of their mouth. Hence it may look like a fish is gulping for air, but it is really harnessing oxygen through its gills.
How Can A Fish Drown?

As eluded to earlier, a fish may drown, or more accurately suffocate, when it does not receive enough dissolved oxygen to its body to stay alive. First you should understand that a fish needs a lot less oxygen, on a per-weight basis, than a human. This is because fish are cold blooded creatures, unlike humans.
Fish do not burn calories just to stay warm, instead they extract whatever heat they can from their environment. Cold-blooded creatures have a much slower metabolism than warm blooded animals like us, so they require less oxygen.
It also means that their activity levels and speed of response is directly proportional to the outside temperature, so during the cold months their metabolism may drop to almost nothing.
Different Ways of Drowning
There are a few different ways by which a fish, especially in an aquarium can die by lack of oxygen.
Oxygen Depletion In The Tank
Firstly, the most common way is due to oxygen depletion in the tank. Fish use up oxygen and expel waste carbon dioxide into the tank.
A tank will exchange oxygen with the air above it if the top is left open, but in small, confined tanks there may not be enough area to exchange sufficient amounts of oxygen to keep the DO levels up. This could lead to oxygen depletion.
In these circumstances it is very important to regularly introduce new oxygen. This could be done by forced oxygenation, circulation, regular water changes, or other methods.
You should also be aware that other creatures in your tank could compete with your fish for the dissolved oxygen present.
For example, certain types of algae love dissolved oxygen, and they will quickly bloom and take all the precious oxygen for themselves. This could be detrimental not just for any fish present in your tank, but for the ecosystem in general.
There are a few other methods which could cause a fish to drown, but they are a bit rarer.
Damage Of The Gills
If the gills of a fish become damages, then their ability to extract oxygen from the water could be extremely compromised, and this could lead to illness and possible death.
This kind of injury could be caused by fights with other similar sized or larger fish, parasites in the water, or interaction with the environment. In any case you should monitor your fish carefully for illness or injury, and if in doubt, consult an expert for advice.
Rely On ‘Ventilation’
One final source of oxygen deprivation occurs in fish that rely on ‘ventilation’. These creatures need forward motion to open up their gills fully, so that they can extract sufficient levels of oxygen from the water.
Sharks are one famous example of this type of fish, although you’re unlikely to keep a shark in your domestic aquarium!
If you do have one of these types of fish though, make sure that your tank is big enough so that they have plenty of space to propel themselves forward in, so they can breathe happily.
What Can I Do To Prevent Fish From Drowning?
Now that you know the answer to ‘can fish drown’ you probably want to know what are the best ways to stop this happening in your own tank.
Stopping illness or injury from damaging your fish’s gills can be hard, but you should make sure all the fish breeds in your tank are peaceful and compatible with each other. Also remove any hazards from the tank such as jagged rocks, and treat regularly for parasites.
Keeping the DO level up in your tank should be a priority. This can be done in a number of ways. For example, installing a filter system with an integrated pump will not only help keep your water clean and clear, but it will also increase the circulation of the water and pull fresh oxygen in.
[amazon box=”B07CN9SG8K”]
You could also install a small air-stone with a pump to bubble fresh oxygen into the water. If you want to avoid installing more pumps, due to the circulation currents formed, then consider placing some aquatic plants in your aquascape. These plants can take in carbon dioxide, photosynthesize it, and release much needed oxygen back into the water.
Best Airstone for Aquarium! Let it Bubble
13 Best Freshwater Aquarium Plants Reviewed
Conclusion
In summary, the answer to the age-old question, ‘can fish drown’ is a firm yes, although it may be better to refer to it as suffocation. Like most animals, fish need plentiful supplies of oxygen so their cells can continually respire and function properly.
The only difference between fish and land-based creatures like us is how we harness this oxygen from the environment. Fish rely on their gills to extract dissolved oxygen from the water, which is then transported to cells around their body.
A fish is in danger of suffocation if its gills are damaged or the levels of dissolved oxygen in a tank become suddenly depleted. This can occur due to lack of oxygenation from a pump failing, growth of algae in a tank, and many other reasons.




